Eliminate uncertainty around host cell protein process impurities.
Various expression systems are used in the manufacturing of biologic therapeutics and vaccines. It is well known that despite recent improvements to purification processes, these products may contain residual impurities, or host cell proteins (HCPs), that can present a substantial immunogenicity risk for patients even at low levels. To minimize detrimental impacts on product immunogenicity, efficacy, and safety, it is critical to identify, assess, and remove excessive HCPs. Therefore, the presence and risk of these impurities should be addressed early in the product characterization process to help set acceptable HCP limits for each product.
As a solution, EpiVax offers ISPRI-HCP™: a fee-for-service report generated by expert scientists using in silico algorithms within the extensively validated ISPRI™ Toolkit to assess the immunogenic potential of contaminant HCPs derived from Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO), E. coli, and other common or proprietary expression systems.
The ISPRI-HCP™ report evaluates the likelihood of anti-HCP antibody responses based on your submitted protein sequences by evaluating and quantifying T cell epitope density and relative conservation with similar T cell epitopes in the human proteome. This ultimately allows for the identification of HCPs that represent a potential risk for immunogenicity and should be removed, while also highlighting those that are more human-like and likely to be tolerated if administered with the drug product.
Recent Publication:
Immunoinformatic Risk Assessment of Host Cell proteins During Process development for Biologic Therapeutics. The AAPS Journal. 2023.
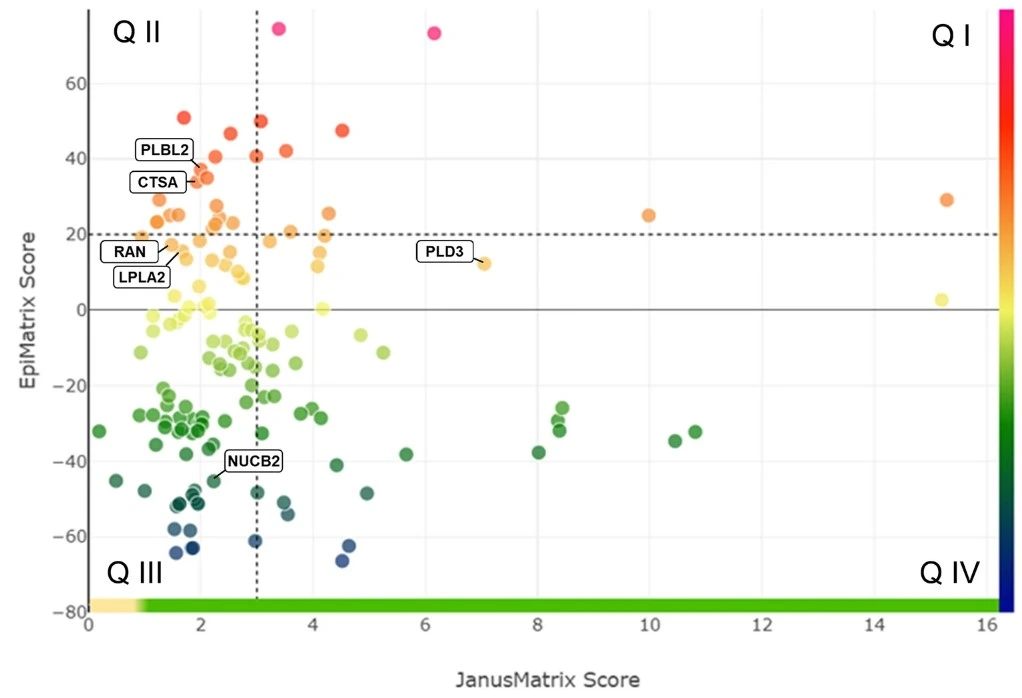
ISPRI-HCP™ Bubble Plot
The plot to the left represents an ISPRI-HCP™ analysis of a typical CHO HCP Landscape. Using a list of commonly found CHO protein impurities, we calculated their EpiMatrix® (EMX) and JanusMatrix (JMX) scores for each protein. Shown here are 143 CHO HCP impurities. Proteins are shown on a gradient scale from high (orange), medium (yellow), and low (green) immunogenicity. Proteins with EMX greater 20 and JMX scores less than 3 are predicted to be high risk (Q II). Proteins with EMX less than 20 and JMX greater than 3 are predicted to be low risk (Q IV).