PANDA Screening
Peptide Abbreviated New Drug Application (PANDA)
Current FDA guidelines on synthetic peptide drugs mandate that pharmaceutical manufacturers of generic drugs provide information that mentions potential impurities in the drug formulation. As their recently issued draft states, for each new specified peptide-related impurity that is no more than 0.5 percent of the drug substance, the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) applicant must characterize the impurity and provide a justification for why such impurity does not affect the safety or effectiveness of the generic synthetic peptide. This justification must include data that supports the claim that any differences in impurities between the proposed generic synthetic peptide and the Reference Listed Drugs (RLDs) do not modify the immunogenicity risk of the product.
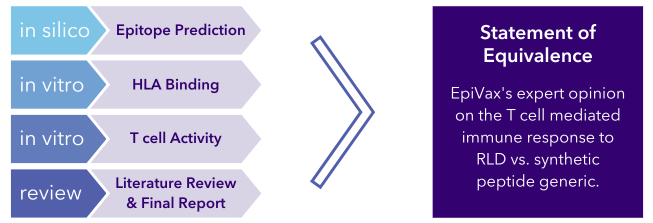
PANDA, EpiVax’s proprietary Peptide Abbreviated New Drug Application screening, is a multi-step approach to assessing the immunogenicity of RLDs, corresponding synthetically-produced generic peptide products and their process-related peptide impurities to evaluate bioequivalence. These steps include an initial assessment with EpiVax’s proprietary in silico toolkit followed by validation of the resulting predictions with in vitro laboratory assays and lastly, a full literature review.
The PANDA approach is used by many clients for immunogenicity screening in the context of seeking FDA approval for generic peptide products. Clients leveraging the EpiVax PANDA approach have submitted and successfully gained approval with the FDA, as well as other global regulatory agencies such as the EMEA(European Union) and Health Canada.
Phase 1: In Silico PreDeFT Immunogenicity Analysis
The Pre-Deimmunization of a Functional Therapeutic (PreDeFT) report is a concise description of each input sequence’s immunogenic potential. Immunoinformatics experts at EpiVax will use the applicable ISPRI (Interactive Screening and Protein Reengineering Interface) tools to analyze the sequences of the synthetically-produced generic peptide product, along with any process-related peptide impurities. Briefly, EpiVax will parse the input sequences into overlapping 9 amino acid frames and evaluate each frame for its binding potential to a panel of Class II HLA allele “supertypes”, which represent 95% of the global human population. Using the EpiMatrix algorithm, EpiVax will produce overall and regional assessments of T cell-dependent immunogenic potential, and screen putative T cell epitopes for cross-conservation with the human proteome using JanusMatrix. EpiVax will then compile the results into a report describing our findings with respect to the predicted immunogenicity of the input sequences.
Recent publication: Immunogenicity risk assessment of synthetic peptide drugs and their impurities
