COVID-19 Coverage
EpiVax continues to drive science forward with several COVID-19 vaccine program efforts. Please follow our coverage here for updates on vaccine development, both local and global, as well as media coverage and important public health information.
UPDATE July 29 2022: Omicron BA.5 Variant and the Persistent Pandemic
First identified in May 2022, the BA.5 Omicron COVID-19 variant now makes up over 80% of positive cases in United States. While evidence is mounting that this particular variant does not cause more severe illness than other circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants, it does come at at time when immunity from initial vaccine doses and prior infection is waning for many Americans.
In March, the FDA authorized 4th booster shots for older citizens more at risk for severe outcomes and death. However it remains to be seen whether additional boosters of currently approved vaccines will be indicated for young, healthy individuals.
There are many signs that the current approved vaccines, while still effective, have some weaknessess against these new variants like Omicron BA.5. In particular, the NIH released a memo this month cautioning that the antibody response from the approved vaccines wears off relatively quickly, especially in the face of these new variants. This comes on the heels of an open letter from academic and industry scientists to the FDA, asking that future vaccine trials include T cell response as a correlate of immune protection. Memory T cell response is an important factor for long-term immunity from viruses. However in the rush to develop vaccines, the global pandemic response focused on triggering a robust antibody response.(Very understandable, considering this is the traditional pathway for vaccine approval!) It can also not be stated enough that the approved vaccines (Pfizer, Moderna, J&J, etc) are an amazing accomplishment and responsible for saving millions of lives.
However, there is a growing consensus that new, improved vaccines are needed for this next stage of the pandemic. In fact, FDA asked vaccine developers to focus efforts on “variant-specific” boosters to target Omicron BA.4 and BA.5
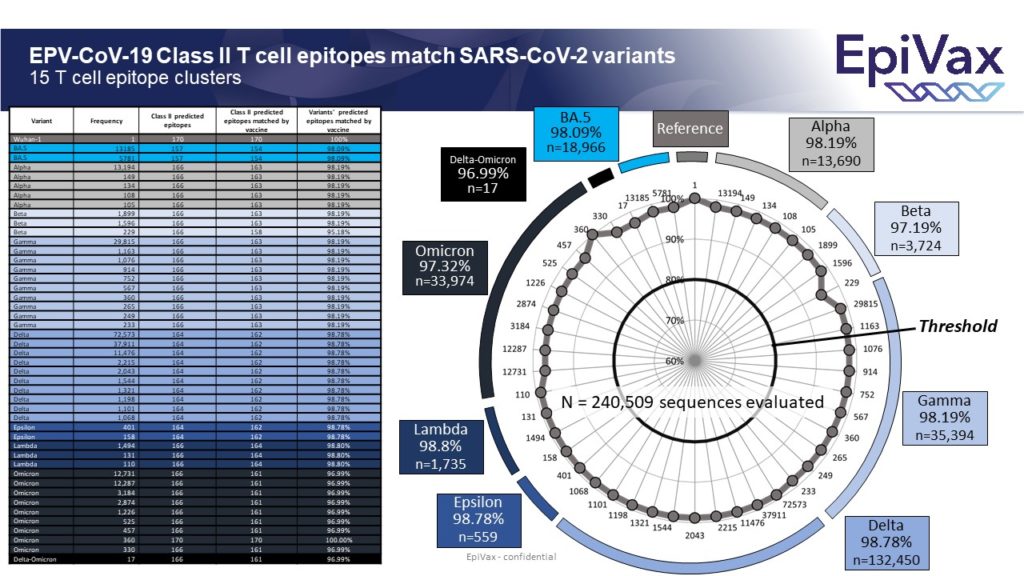
So, you may ask… what about EpiVax’s T cell driven vaccine candidate, EPV-CoV19? We have continuously updated our expected efficacy data as new variant sequences emerge. As you can see below, our candidate is predicted to hold up quite well against Omicron BA.5, as well as all previous variants.
Behind the scenes, we continue to make progress towards clinical trials! We look forward to sharing updates on this topic very soon.
UPDATE January, 11 2022: Omicron Variant surges in U.S.
The highly contagious omicron variant, first documented in the U.S. in November 2021, is surging in the U.S. Today, total hospitalizations in the U.S. exceeded records hit last January, when vaccines were not widely available.
EpiVax conducted an analysis of our T cell driven COVID-19 vaccine, EPV-Cov19 quickly after the Omicron sequence was released. We are pleased to report that our candidate is predicted to have 98.2% epitope conservation against Omicron, which is on par with our analysis against every other SARS-COV-2 Variant of Concern (VOC).
As we enter the third year of the pandemic, the discussion about T cell driven vaccines against COVID are heating up. Alessandro Sette and colleagues recently released a paper on the benefit of a T cell vaccine (Like EPV-CoV19) over the current spike-driven shots. And it was nice to see CBS news dedicate some time to subject yesterday.
EpiVax is continuing to advance our COVID-19 vaccine to the clinic, as you can see in this recent press release. More updates to come very soon!
UPDATE July 7, 2021: Delta Variant now dominant U.S. COVID-19 strain
The U.S. reached this notable but not unexpected milestone just before the 4th of July. This strain first appeared in India and is now distributed globally. We’ve seen this before with other strains, they quickly become prevalent only to be replaced by newer variants. All part of the cycle for this quickly evolving virus.
The Good News:
Multiple studies have now shown that current vaccines hold up well against the Delta Variant. One study from Israel points to a small decrease in efficacy, but nothing to cause alarm.
Something to keep an eye on:
This variant is more contagious than previous iterations, 60% more transmissible than the Alpha Variant that previously most prevalent in the U.S.
The vast majority of new infections and hospitalizations are unvaccinated people, and there is a growing regional component in play. Broadly, the Southern and Western states have lower vaccination rates than other regions (New England for example). However even within states that have high vaccination rates, there are pockets with lower vaccination rates. Therefore all areas should be concerned about new variants.
We may see geographically patchy spikes in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially going into the fall/winter and especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
COVID Vaccine Research needs to continue:
The persistence of SARS-COV-2 in global communities is becoming a long-term reality. And the massive amount of unvaccinated people means that new variants will continue to appear. The potential that future variants may respond to current approved vaccines is an uncomfortable but necessary thought.
That’s why here at EpiVax, we’ve been tirelessly pushing forward our research on a T cell driven COVID-19 vaccine. In fact, our vaccine candidate EPV-CoV-19 is predicted to be effective against all known variants. And a T cell driven vaccine, in conjunction with an antibody driven vaccine (ie Pfizer, Moderna, Johnson & Johnson, etc) could be the most effective and long-lasting vaccination combination. The different mechanisms of action have the power to drive a robust, yet targeted, immunity.
UPDATE APRIL 7, 2021: Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccines are effective at preventing COVID19 infection
One of the most important lingering questions about COVID-19 vaccination was whether immunized people could contract the virus, and subsequently transmit the virus to others.
According to a ground-breaking paper released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention last week, the vaccines are 90% effective at preventing COVID19 infection for fully immunized people, and even 80% effective for those having only received 1 of the 2 required shots for the mRNA vaccines approved in the U.S. (Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech).
To quote Mark Thompson and team who published the paper, “These findings indicate that authorized mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are effective for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection, regardless of symptom status, among working-age adults in real-world conditions.”
Great news indeed, with huge epidemiological implications. Not only do vaccines drastically reduce the risk of severe sickness, hospitalization and deaths, they also reduce the person to person spread responsible for dragging out the pandemic.
Fun fact, Annie De Groot, CSO/CEO of EpiVax worked with closely with members of this research team during her time at the National Institutes of Health in the late 1980’s!
Congratulations to Mark and team, very welcome news. Read the full paper here.
UPDATE March 19, 2021: Vaccine boosters for long-term immunity
Vaccine roll-out is in full swing in the U.S. According to Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus resource center, 11% of the population is fully-vaccinated, and 25% have received at least one shot.
Great news, and lines up with the U.S. policy goal of having vaccines available to all adults by the end of May.
In the scientific community, our focus now shifts. Will vaccine efficacy wear off after 6 months? A Year? Will we get COVID-19 shots each year like we do with Influenza?
There is so much we do not know about SARS-COV-2 vaccine efficacy in the long-term. The consensus is that some sort of booster treatment will be needed to maintain immunity. Combination trials are underway to see if it would be safe and effective to take combinations of vaccines. If you initially got the Moderna mRNA vaccine, can you then take the Johnson & Johnson Adenovirus-based shot several months later? We will soon know the answers.
Writing for The Scientist, Asher Jones correctly calls out the need for a robust immune response, by activating T cells in addition to antibodies. Combining different vaccine treatments is actually an opportunity to create a more effective, longer-lasting treatment and is an opportunity to bring in new vaccines that illicit a T cell response. EpiVax’s EPV-CoV19 vaccine is perfectly matched for this use! So while these combo studies are conducted in part for safety due diligence, the resulting improvement in efficacy is just as important.
EpiVax CEO/CSO, Dr. Annie De Groot weighed in on LinkedIn last week.
We think the best way to ensure a robust T cell response is a T cell driven vaccine😊
UPDATE March 1, 2021: Lessons from HIV research for SARS-COV-2 vaccine design
Big vaccine news this week! The Johnson & Johnson SARS-COV-2 vaccine performed positively according to results from the FDA. Expect FDA emergency use authorization imminently! This will give the world another vaccine to use, a much needed development.
Prior to the pandemic, Johnson & Johnson had been very involved with research into HIV vaccines. In fact, their SARS-COV-2 vaccine builds on adenovirus-based vaccine research first conducted in the HIV space.
Foundational vaccine research (especially into constantly mutating viruses such as HIV and Hepatitis C) has enabled the quick approval of the SARS-COV-2 vaccines. In fact, EpiVax CEO/CSO Annie De Groot sat for an interview with Michael Dumiak for the August 2020 issue of IAVI, to discuss the lessons she and other researchers learned from HIV work and applied to COVID-19 response.
Check out the full story here!
UPDATE February 24, 2021: COVID-19 Researchers Unite!
It’s a busy time for International COVID-19 summits. LOTS to discuss. The vaccine roll-out is accelerating, which is great news! Unfortunately, the incidence of COVID-19 variants is also rising. The next few months will see a lot of activity as scientists and healthcare workers scramble to keep new infections down.
Here are two recent events every COVID-19 researcher should be aware of. We’ll add recording links here as they are released.
4th ISV Congress – COVID-19 Vaccines Update – February 10, 2021
This was an excellent level-set from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, International Society for Vaccines, and most companies with approved vaccines, including Moderna, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and the Gamaleya National Research Center in Russia.
The main topic was safety and efficacy of the vaccines already in use. Good news is that these vaccines are safe! The question of efficacy of vaccines in relation to variants is more complex, but each company shared out what they could.
The full Conference is available for free here: 4th ISV COVID-19 Vaccines Virtual Congress – YouTube
COVAX Workshop – February 25, 2021
COVAX is the vaccines arm of the World Health Organization(WHO) COVID-19 response. Nice overview here.
COVAX is hosting a Workshop February 25, 2021: Immune Correlates, SARS-CoV-2 Variants and ‘mix & match’: How vaccine developer approaches might be impacted by emerging data
This will be an important meeting, expect discussion to focus on the new SARS-COV-2 variants, and recommendations for improving the immune response for existing and future vaccines.
Notably mentioned, identifying “the most suitable immune marker to infer efficacy.” Up to this point neutralizing antibodies have been front and center. However COVAX acknowledges T-cell response could play an important role. EpiVax’s COVID-19 vaccine program is focused on generating T-cell response to confer immunity.
UPDATE February 4, 2021 Publication Alert: Characterization of pre-existing and induced SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8 + T cells
Almost a year into the COVID 19 pandemic, and the scientific research community continues to learn more about the virus. Recently an important paper was released in Nature Medicine on the characterization and prevalence of memory CD8 + T cells in patients with SARS-CoV-2 prior, during, and following infection.
Isabel Schulien and team at the University of Freiburg observed memory CD8+ T cell responses in ex vivo analysis and human patients recovering from infection to characterize dominant T cell epitopes associated with SARS-CoV-2. Especially interesting is that the authors conducted a longitudinal study of recovering patients. Virus-specific CD8+ T cells were detectable even after patients became seronegative for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. This is an important building block to understanding how T cell response will play into immune protection for individuals that have already had the virus, and how T cell based vaccines can be a vital pathway to long-term immunity. For more information about our T cell based vaccine click here
Access the full publication here
UPDATE December 31, 2020 Press Release: EpiVax and EpiVax Therapeutics Advance COVID-19 Vaccine Program, EPV-CoV-19
EpiVax (“EpiVax”) and EpiVax Therapeutics (“EVT”) provide a status update on EPV-CoV-19, their peptide-based COVID-19 vaccine.
EPV-CoV-19, a T cell epitope-based vaccine designed by EpiVax’s scientists in February 2020 and licensed to EVT in August 2020, has completed IND-enabling preclinical validation studies and is on the verge of clinical trials, slated for April 2021. Phase I clinical trials will take place in the U.S., as well as in parallel at two sites internationally.
With the recent headlines about COVID-19 variants, development of a vaccine that stimulates a T cell response associated with long-term immunity remains critically important.
T cell-directed vaccines for COVID-19 are expected to reduce the impact of COVID-19 infection and prevent severe disease. While mutations to the spike protein (see new UK variant, VOC 202012/01 or B.1.1.7) may eventually reduce the efficacy of antibody-directed vaccines, this would be less true for T cell epitope-directed vaccines like EPV-CoV-19, which are designed to provoke long-lasting immunity against multiple proteins.
Read the full press release here.
UPDATE September 23, 2020 Dr. Lenny Moise talks COVID19 with local Venture Cafe
EpiVax’s Vaccine Director Dr. Lenny Moise was invited to participate in the Venture Cafe Providence’s #VCVIRTUAL panel on Thursday September 17th. I encourage you to watch the full session, but Dr. Moise’s contribution begins at ~36:10 into the recording, should you want to jump ahead.

PRESS: Sepember 28, 2020 – EpiVax’s promising vaccine candidate for COVID-19 moves ahead ConvergenceRI
A feature in the Monday morning copy of ConvergenceRI views EpiVax as a hot topic in the growing competition of weekly Zoom conferences.
“But perhaps the most far-reaching, informative session on Zoom on Friday morning was a webinar offered by EpiVax, providing an update on its COVID-19 vaccine development efforts. The company, one of Rhode Island’s pioneer biotech firms launched 22 years ago, has now pivoted many of its resources to work on manufacturing a T-cell, epitope-driven vaccine, with the goal of initially targeting the vaccine to protect front-line health care workers as the first priority.
Read the full publication here.
If you missed the EPV-CoV-19 update session, please register here for the recording.
UPDATE June 2, 2020 Press Release: Intravacc and EpiVax team up in development of COVID-19 emerging vaccine
Press Release: Intravacc and EpiVax team up in development of COVID-19 emerging vaccine
Intravacc, one of the world’s leading translational research and development vaccine institutes, and EpiVax, a biotechnology company with expertise in developing vaccines and therapeutics, announce that they have entered into a collaboration agreement to further progress an novel vaccine against COVID-19, based on Intravacc’s proprietary Outer Membrane Vesicles® (OMV) technology platform.
Intravacc will combine its safe and immunogenic OMV delivery platform with synthetically produced COVID-19 epitopes (protein allergens), designed and optimized by EpiVax using advanced immunoinformatics tools, in order to generate a safe and highly effective T-cell response against SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses.
Annie De Groot, MD, CEO and CSO of EpiVax, said:
“We are thrilled to enter into a partnership with Intravacc using their very novel ‘click-on’ OMV technology and the highly immunogenic and safe SARS-CoV-2 multi-epitope-bearing peptides designed using the iVAX toolkit at EpiVax. We believe that the combination of technologies and the strength of our longstanding collaboration with Intravacc will lead to the development of an effective and safe vaccine that could rapidly benefit hundreds of millions of people around the globe.”
Pre-clinical studies will start immediately so as to select the best candidate peptides for the vaccine. Intravacc will utilize its in-house pilot-scale facility for the GMP production of the OMV-peptide vaccine, for clinical (phase I) studies expecting to start in Q4 2020.
Read the full press release here.
UPDATE April 28, 2020: Press Release: Entos Pharmaceuticals partners with EpiVax to develop a pan-coronavirus DNA vaccine
Press Release: Entos Pharmaceuticals partners with EpiVax to develop a pan-coronavirus DNA vaccine
Entos Pharmaceuticals (Entos), a healthcare biotechnology company that develops next generation nucleic acid medicines using the Fusogenix drug delivery platform, today announced a collaboration with EpiVax, Inc. (EpiVax), a world leading informatics and immunology biotechnology company with a proven track record in vaccine development.
This partnership will combine the Entos Fusogenix DNA delivery technology with optimized COVID-19 epitopes from EpiVax to generate a highly effective immune response against the novel coronavirus, while ensuring a high degree of safety.
“We are excited to be working with the exceptional team at EpiVax, whose computational approach to optimizing vaccine design is second to none,” said Dr. John Lewis, CEO of Entos, “We’re looking forward to bringing an effective DNA vaccine to human clinical trials as soon as possible.”
Read the full press release here.
UPDATE April 14, 2020: SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Status Report
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Status Report
A perspective published 14Apr2020 in Immunity
As confirmed COVID-19 cases and mortalities rise, the focus remains heavily on vaccination and treatments. Many companies are racing to clinical trials with the vaccine they believe will be “the one”. But will it be the right one?
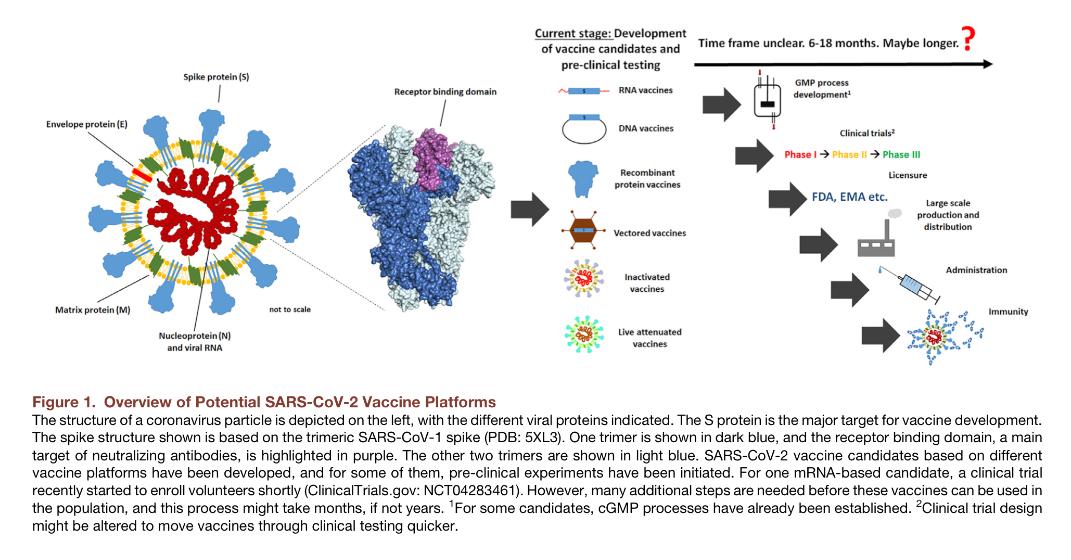
EpiVax continues to focus on an epitope driven vaccine approach that will avoid Antibody Dependent Exacerbation (ADE).
UPDATE April 10, 2020: Immunomic Therapeutics, EpiVax and PharmaJet to Develop Novel Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19
Press Release: Immunomic Therapeutics Forms Collaboration with EpiVax and PharmaJet to Develop Novel Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19 Using its Investigational UNITE Platform
Immunomic Therapeutics will work with leaders from EpiVax and PharmaJet, who have a wealth of immunology and vaccine delivery expertise, to rapidly develop its COVID-19 vaccine. Immunomic’s UNITE platform has been widely applied to create vaccine candidates for rabies, yellow fever, dengue fever, hepatitis C and SARS, a relative to the SARS-Cov-2 coronavirus.
EpiVax CEO, Dr. Annie De Groot, said “My company is thrilled to partner with ITI and PharmaJet on this important project. We believe that the UNITE platform, combined with epitopes that have been carefully triaged by EpiVax’s advanced computational tools, will generate a highly effective immune response against the pathogen that causes COVID-19, while reducing off-target effects.”
This collaboration will combine leading technologies from all three companies: Immunomic’s UNITE platform, EpiVax’s in silico T cell epitope prediction tool, and PharmaJet’s well established Tropis® Needle-free Injection System that precisely targets delivery to the intradermal tissue layer. By bringing these companies’ and their technologies together, Immunomic aims to create a vaccine against COVID-19 that produces broad and potent immune responses, is feasible for rapid-responses, scalable, thermostable, safe and easy to administer by healthcare professionals.
UPDATE April 8, 2020: EpiVax announces GAIA Vaccine Foundation Partnership
EpiVax Partners with GAIA Vaccine Foundation to Make COVID-19 Vaccine License Free to Developing Countries
EpiVax, Inc., is using advanced computational tools to accelerate a COVID-19 vaccine candidate (EPV-CoV19) for healthcare workers (HCW) into clinical trials in 6 months. Today, EpiVax announces its partnership with GAIA Vaccine Foundation (“GVF”) to crowd-source funds for the project and its pledge to make a free license available to developing countries who qualify, in the context of this partnership.
Annie De Groot, MD, EpiVax CEO/CSO, states “The soul of each company will be revealed during this crisis. Personally, I do not believe this is the time to become a billionaire. Each of us should do what we do best to reduce the impact of COVID-19 globally.”
GVF, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, will enable private citizens and foundations to contribute to development of EPV-CoV19. GVF’s mission is to reduce incidence of infectious diseases that disproportionately affect the under-served and promote the development of globally relevant, accessible vaccines that can be distributed on a not-for-profit basis in the developing world.
Read the full press release here.
UPDATE April 7, 2020: Epitope Driven Vaccine Design, How We Got Here
EpiVax had a vaccine design ready within 3 hours of SARS-CoV-19 genome publication
EpiVax’s flagship immunoinformatics software iVAX consists of a suite of immunoinformatics tools for the design of epitope driven vaccines. Co-founders Dr. Anne De Groot and Bill Martin, along with bright-minded scientists at EpiVax, have worked for over 22 years to develop these tools.
We are proud to share the publication of : Better Epitope Discovery, Precision Immune Engineering, and Accelerated Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Tools in frontiers in Immunology
This publication gives comprehensive overview of the technology and methodology that went into EpiVax’s novel EPV-CoV19 epitope driven vaccine design.
UPDATE April 6, 2020: Testing for COVID-19
When should you get tested for COVID-19?
The CDC continues to update its recommendation of testing for COVID-19 infection. At the time of this publishing, there is still no treatment approved for mild COVID-19 infection and a positive test result may help you inform decisions about who you come in contact with. For more severe cases, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
From the CDC webstie:
In the United States, many states have expanded testing opportunities in recent weeks/days. The pharmacy giant CVS, which began right next door in Lowell, Massachusetts, announced today that it will be offering “drive-through” testing in Rhode Island and Georgia. To see if you qualify for CVS rapid testing in your state, click here.
Read the complete CDC recommendations here.
UPDATE April 1, 2020: Coronavirus Business Tracker: How The Private Sector Is Fighting The COVID-19 Pandemic
Forbes magazine online publication by Giacomo Tognini
Read the full article here.
Relief efforts large and small are continuing to expand around the globe. Companies of all sizes are pivoting focus to prevention, treatment and recovery from COVID-19 transmission. While there has been a massive shift in many biotech pipelines, there are many other notable contributions from clothing and cosmetics manufacturers to beer companies and mattress makers.
EpiVax is proud to be named as one of the companies stepping up to aid in this global effort.
“EpiVax: Providence-based immunology firm is working with the University of Georgia and Miramar, FL biotech outfit Generex on separate COVID-19 vaccine efforts.”
*EpiVax would like to add our newest vaccine collaboration with eTheRNA.
UPDATE March 31, 2020: How soon will we have a coronavirus vaccine? The race against covid-19 by Carrie Arnold
How soon will we have a coronavirus vaccine?
The race against covid-19 by Carrie Arnold
Read the full article here.
New Scientist recently published an article addressing the need for novel, out of the box approaches to making a vaccine faster than ever before.
Carrie Arnold writes “To speed things up, scientists are turning to untested classes of vaccines, and rethinking every part of how they are designed, evaluated and manufactured. If the approach works, we will, for the first time, have identified a new disease and developed a vaccine against it while the initial outbreak is still ongoing.”
Arnold highlights EpiVax’s computational modeling technology as a leader in getting a head start on vaccine design for the novel coronavirus. Within hours of the gene sequence being published, EpiVax had identified key regions to target for vaccine development. EpiVax CEO and Co-founder Dr. Annie De Groot explains that this application for the technology has been a long time coming. “It took us 21 years of work to be able to develop a vaccine in 3 hours” says De Groot.
Vaccine developers around the world are in a race against time to rapidly design, produce and test a new vaccine. At the time of publishing, at least 35 candidate vaccines, six backed by CEPI, have been filed. The unprecedented 12-18 month timeline has many hurdles to overcome; most recently an Ebola vaccine broke records by being ready in five years. “All these steps are hard enough when there isn’t an outbreak, says De Groot, and no one can say how the pandemic will affect supply chains and labour pools related to vaccine development. It is also possible that, by the time a vaccine is ready for late-stage clinical trials, there won’t be enough virus circulating to provide firm answers about its efficacy.”
EpiVax continues to forge a patch forward, working with a number of collaborators on vaccine designs. We are up to the challenge and remain dedicated to being a part of the solution.
UPDATE March 30, 2020: CEO/CSO Dr. Anne De Groot sits down with the Boston Globe
The Boston Globe’s weekly Ocean State Innovators column features a Q&A with Rhode Island innovators who are starting new businesses and nonprofits, conducting groundbreaking research, and reshaping the state’s economy.
This week’s Ocean State Innovators conversation is with Dr. Anne S. “Annie” De Groot, founder and CEO of EpiVax Inc., a Providence biotechnology company working on a coronavirus vaccine.

UPDATE March 25, 2020: Epitope-driven vaccines
Immune responses to viral infections can sometimes be detrimental to the host. While some viral antibodies are beneficial (anti-viral), others can actually be virus-aiding. They allow the virus access to cells through non-traditional pathways such as the Fc-receptor. This is called antibody dependent enhancement (ADE).
EpiVax is developing, among many others, an epitope-driven vaccine against CoV-SARS-2. These novel vaccine candidates focus the immune response on specifically creating T cell memory to CoV-SARS-2. This strategy likely minimizes the B cell and antibody response compared to whole antigen/whole pathogen vaccine formulations, thereby significantly reducing the risks associated with ADE.
Read more about EpiVax’s approach on epitope-driven vaccine design here.
UPDATE March 24, 2020: Press Release: eTheRNA launches an international consortium and starts development of cross-strain protective CoV-2 mRNA vaccine for high risk populations
EpiVax announces it’s involvement in an international consortium for the rapid development of a mRNA vaccine for high risk populations, which include health care workers and families of those with confirmed cases.
The partnership formed between EpiVax, aTheRNA, Nexelis, REPROCELL and CEV will utilize three technologies:
- eTheRNA’s proprietary Trimix technology: an mRNA-based vaccine adjuvant that stimulates dendritic cells into activating a strong CD4 and CD8 T cell response.
- A combination of T cell epitopes from the virus brought together on a single mRNA construct. For SARS-CoV-2 this will employ an in-silico epitope prediction and design approach from EpiVax Inc. to identify the target.
- An intranasal vaccine delivery platform using a nasal atomizer and a proprietary formulation that delivers the mRNA to the nasal mucosa and optimizes expression. One of the most promising formulation candidates is being repurposed for clinical use in collaboration with REPROCELL.
Read more about the collaboration efforts here
UPDATE March 23, 2020: A Call for Funding
With all proposed collaborations in place, EpiVax is poised to make a great impact on the rapid development of a COVID-19 vaccine. However, the vaccine will not come without funding. The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) has called for $2 Billion USD in immediate government funding for the expansion of vaccine candidates brought to clinical trial, and the increase in chances of success.
EpiVax is happy to share that a request for funding has been submitted to MCDC (DOD). We are eager to be a part of the solution and look forward to continuing driving science forward.
UPDATE March 20, 2020: Rapid Development of Health Care Worker Vaccine
While we continue to pursue multiple vaccine collaborators, one of our top priorities remains health care workers. EpiVax is developing an epitope based vaccine that could be ready in as little as 6 months. Scientists at EpiVax have a plan in place for carrying out this rapid development:
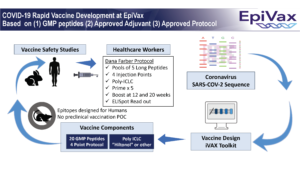
Many vaccines and treatments continue to be developed and EpiVax is proud to be on the forefront of these efforts. You may find a complete list here
Vaccines
- EpiVax and Generex, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- EpiVax and UGA, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- Moderna Therapeutics, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Phase 1
- CanSino Biologics, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Phase 1
- Arcturus Therapeutics, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- BioNTech, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- CureVac, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- GlaxoSmithKline, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- Johnson & Johnson, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- Pfizer, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
- Sanofi, Approach: Vaccine, Stage: Preclinical
Treatment therapies
- Gilead Sciences, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Phase 3
- Ascletis Pharma, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Phase 1
- Eli Lilly, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Johnson & Johnson, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Pfizer, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Sanofi, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Takeda, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
- Vir Biotechnology, Approach: Treatment, Stage: Preclinical
UPDATE March 19, 2020: EpiVax seeks Federal Aid for Funding of COVID-19 project: WPRI 12 Interview
EpiVax is currently working on a COVID-19 vaccine tailored specifically for healthcare workers. In an interview with WPRI 12, Dr. Anne De Groot stated: “They’re the first line of defense against the virus, so we want to give them something that will actually generate what we call ‘immune system body armor.” It remains critical to EpiVax’s mission to develop this vaccine.
One major hurdle: funding.
EpiVax is currently petitioning for $300 million USD in government aid to follow through with the proper safety and efficacy testing needed to make this vaccine available as rapidly as possible.
UPDATE March 18, 2020: Identifying Vaccine Candidates: NBC 10 Interview
Dr. Anne De Groot speaks with local NBC 10 News‘ Tamara Sacharczyk about EpiVax’s continuing efforts to develop a COVID-19 vaccine. Dr. De Groot outlines the importance of EpiVax’s proprietary computer tools for rapid identification of vaccine candidates. EpiVax maintains hope that with a peptide based vaccine, Phase 1 trials may begin in as little as 5 – 6 months.
UPDATE March 17, 2020: Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO)'s featured leaders in vaccine development for Coronavirus
EpiVax is proud to be one of Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO)’s featured leaders in vaccine development for Coronavirus.

UPDATE March 16, 2020: EpiVax Shares Plan to Keep Employees and Clients Safe
As closures and cancellations increase across the state and across the country, we encourage you to remain calm, collected, and informed. Dr. De Groot recently shared some wonderful information on public action in times of pandemic.
At EpiVax, we are taking precautions. As the public health threat escalates, we want to assure you that EpiVax has implemented all precautionary measures recommended in the Guidance for Businesses and Employers to Plan, Prepare and Respond to Coronavirus Disease 2019 developed by the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control (CDC). Please feel free to reach out to us by emailing info@epivax.com with any questions or concerns.
Check out Dr. De Groot’s blog, Thinking Out Loud for our preparedness plan.
UPDATE March 14, 2020: EpIVax's plans to develop a vaccine for COVID-19: 20h on France 2 Interview
On Saturday 14Mar 2020 our CEO/CSO Anne De Groot was featured on 20h on France 2 with host Anne-Sophie Lapix. describing EpIVax’s plans to develop a vaccine for COVID-19.
UPDATE March 4, 2020: EpiVax: Working as Fast as We Can
We’re working as fast as we can. Currently, the EpiVax Vaccine Team (Lenny Moise, Annie De Groot, Christine Boyle, and Lauren Meyers) are designing vaccines for four different efforts – Peptide-based vaccines (Press release HERE); A Spike-based Recombinant Protein vaccine with the University of Georgia (Press release HERE), and we are also looking to partner in RNA and DNA.
Our CEO, Dr. Anne De Groot, has also been asked her professional opinion in several news outlets, including WBUR Public Radio and Providence Business News. Dr. Lenny Moise has also spoken with local Convergence RI about EpiVax’s approach to develop a vaccine.

Researchers working in the labs at EviVax in Providence. From left, Olivia Morin, research associate, Mitchell McAllister, research associate, working in their culture lab. PBN PHOTO/MICHAEL SALERNO
2019-nCOV (Coronavirus): What to know, and what to expect?
February 6, 2020
Unless you have been in a media blackout these past two weeks, you are well aware of the latest public health threat: 2019-nCoV. This new strain of coronavirus is currently linked to over forty-thousand fatalities and rising in China, and additional cases have been brought to other areas of the world by air travelers.
Here’s our perspective…
Is it worse than SARS? That’s hard to say. Younger people may be more resilient, but a reported 25-30% of cases require intensive care. In truth, we don’t know because we don’t have the denominators (number of infected, number recovering), we only have the available daily updates on the situation which are available here.
Isn’t it just like the common cold? Afterall, the common cold is caused by coronaviruses. That would be nice, but, no. Our analysis of the conservation of T cell epitopes found in currently circulating strains of coronaviruses with the novel 2019 n-COV shows poor conservation of T cell epitopes (at left), this is also true for other coronaviruses like SARS, MERS, etc, at right. That’s why this virus is going to be far worse than the common cold or the flu. (For medical updates see here).
Can you make a vaccine for it? Yes we can. And, because it is an RNA virus, has the opportunity to ‘go stealth‘ due to the mutability of its genome, making it a bit more difficult. But we are working swiftly, under the direction of EpiVax Vaccine Director, Dr. Lenny Moise, to develop a computational plan of attack. Important to note – it has human-like sequences that may abrogate immune response. Like HIV. Like HCV. See below a JanusMatrix analysis of the 2019-nCOV spike protein and read see our blog post here.

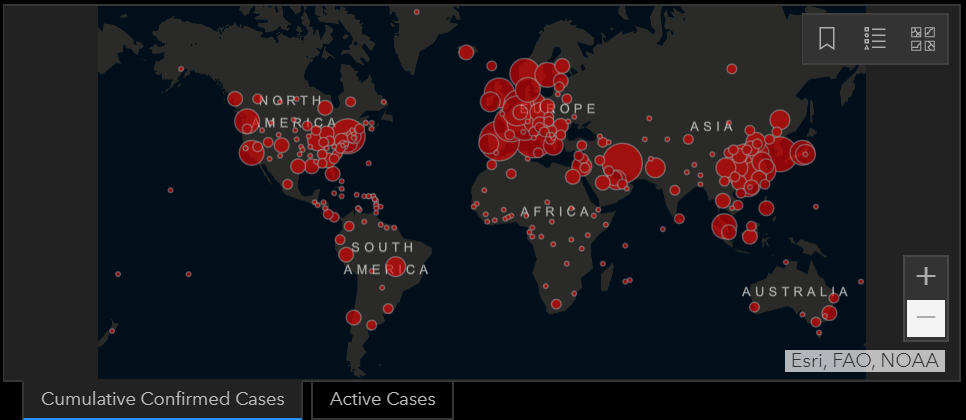
A Live Look at COVID-19 Epidemiology
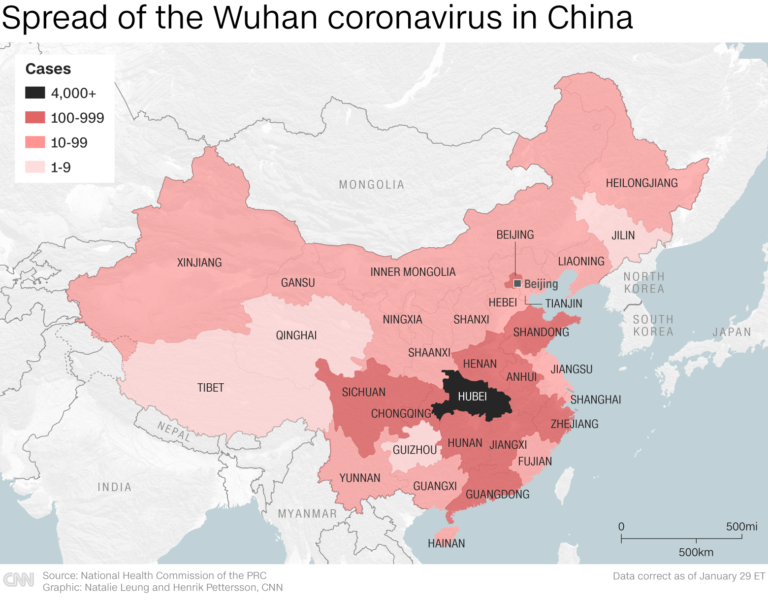
The First Mention of Spread Within China
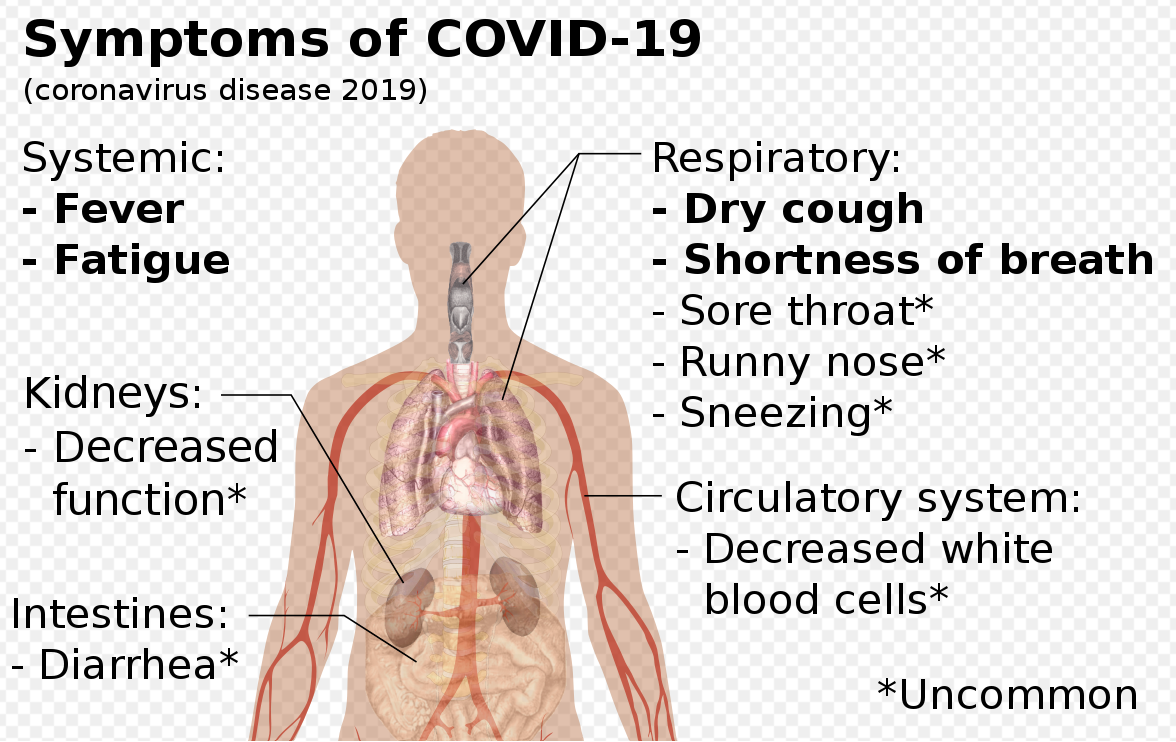
Clinical Characteristics: Case Study in 138 Patients
Join our newsletter
We strive to provide our clients, collaborators and everyday immunology enthusiasts with valuable content. Written by our CEO/CSO Dr. Anne Dr Groot, you can expect up to date vaccine development efforts, upcoming events and so much more from our offices here in Providence, RI.